
What is a w9 form?
IRS Form W-9, is one of many tax documents required by the IRS (Internal Revenue Service) to help contract workers accurately estimate the taxes owed in a given tax year. It is a common IRS form used to provide necessary information to a person or company making payments to another person or company. One of the most typical situations is working as an independent contractor for a business. Businesses use it to obtain tax data from outside sources. Our bookkeeping experts provide comprehensive monthly financial reports about your business to ensure that you stay up to date on what is happening.
Key Points
- Information about taxpayers is gathered using Form W-9 to assist with informational reporting to the IRS.
- Although it is used in other contexts as well, the Form W-9 is most frequently used when working with businesses that employ independent contractors.
- The form requests that a taxpayer enter their name, address, tax bracket, and withholding specifications.
- Due to the sensitivity of the information on Form W-9, all parties should exercise caution when obtaining, sending, and storing the document.
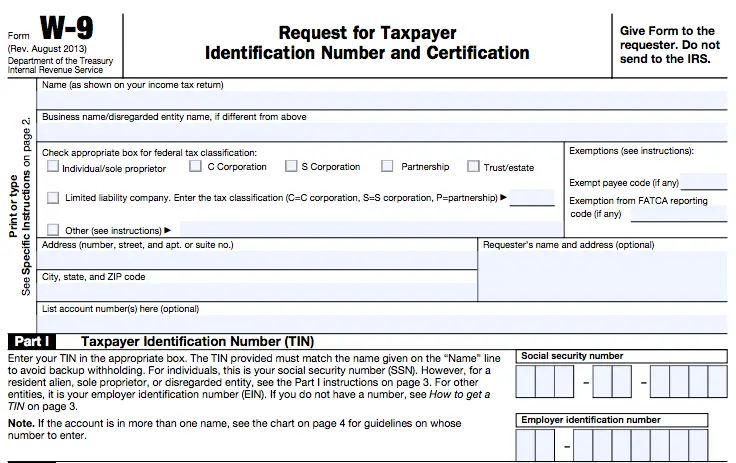
A W-9 form has two sections. The payee's identification information is in Part I. The certification, or signature, in Part II attests to the accuracy of the ID information. It is also known as a "request for taxpayer identification number and certification," though "W-9" is the more common name.
Purpose of Form W-9
A W-9 is used to obtain tax information from a vendor, independent contractor, freelancer or gig worker. A business is required to file an information return when it pays a non-employee or another entity more than $600 for their services in a calendar year. The goal of a W-9 is to obtain all necessary information directly from the service provider in order to guarantee that the information returned is accurate. Even though some information is accessible to the general public, Form W-9 safeguards the company requesting the information by requiring the other party to sign the completed form. The signature attests that:
- The provided tax identification number (TIN) is accurate.
- Backup withholding is not applicable to the other party.
- The opposing party asserts that they are exempt from backup withholding.
- The vendor's FATCA code (as well as their exemption status).
Businesses fill out that information return using the name, address, Social Security number, or tax identification number contractors provide on Form W-9. The IRS should not receive copies from either the sender or the recipient. The company requesting the tax information must also keep copies of the form in a secure location.
Uses of Form W-9
The IRS receives a variety of informational returns that are prepared using the Form W-9. The most typical scenario is when an independent contractor finishes work for a business and gets paid. The independent contractor must receive a Form 1099-MISC and self-report their taxes if they receive more than $600 in a calendar year. The intent behind a Form W-9 goes beyond this particular circumstance. In order to file Forms 1099-INT, 1099-DIV, or 1099-B, a bank or financial institution depends on receiving taxpayer data. A Form W-9 may also be required from a taxpayer in the case of student loans, real estate transactions, and debt cancellation. You can contact us for more detailed information on this.
When to request a W9 Form
Form W-9 is required in order to conduct business with independent contractors and freelancers. You must obtain a W-9 for tax purposes if your business pays non-employees or small businesses more than $600 each for work that has been completed. Your company is exempt from paying Social Security and Medicare taxes, as well as deducting income taxes from payments made to independent contractors. As a result, the IRS needs to know to whom you are paying in order to be able to pursue collection. Use your W-9s to report how much you paid each contractor at the end of the year by keeping them safely stored.
Information needed on Form W-9
Independent contractors must provide the following pieces of information on Form W-9:
- Name: This name will appear on the taxpayer's tax return. This field must be filled out. This field either contains the name of an individual or, in the case of a sole proprietor, the name of the owner. The name of a partnership or other entity may also be listed by the taxpayer.
- Other Business Name: Only if the taxpayer uses a business name, trade name, DBA name, or disregarded entity name is this line necessary.
- Federal Tax Classification: The taxpayer must indicate their legal status as a corporation, an individual, a sole proprietor, an LLC with only one member, a limited liability company, a partnership, a trust, or an estate. The taxpayer is only required to choose one of the available options.
- Exemptions: The taxpayer must decide if they are exempt from FATCA reporting or backup withholding.
- Address: The taxpayer must enter their ZIP code, city, and state along with their address.
- Account Numbers: At the request of the requestor, the taxpayer may provide additional information in this option field. For illustration, a bank or brokerage company might request that the client enter their client information here.
- Part I, Tax Identification Number: The main goal of a W-9 is to obtain the taxpayer's tax identification number. This could be an employee identification number or a social security number.
The taxpayer must sign the form under Part II after providing the aforementioned information (Certification). Form W-9 must be carefully guarded by the person filling it out and the business receiving the completed form during transmission and after receipt to prevent identity theft because it asks for a tax ID or social security number.
Penalties for Non-Compliant Form W-9
For failing to provide or adhere to the reporting requirements of Form W-9, the IRS has specified a number of penalties. For each instance of non-compliance with tax law and regulation, the taxpayer is liable for a $50 file if they fail to provide a valid tax number. If the taxpayer can demonstrate that the non-compliance was not the result of willful neglect, this fine may be waived. If a taxpayer provides inaccurate information that results in inaccurate withholding, they may also be subject to civil penalties. The taxpayer may be fined up to $500 if they knowingly provide false information that prevents backup withholding. Further non-compliance carries heavier penalties, including in some circumstances the possibility of criminal prosecution for the taxpayer. The taxpayer faces fines or jail time for willfully fabricating any declarations or information. The requester of taxpayer information is also subject to penalties. The requestor may face civil or criminal penalties if he or she discloses or uses the taxpayer's TINs in violation of federal law. You can monitor the health of your business with the help of monthly reports created by our certified accountants at our bookkeeping services.
Other Considerations
If an independent contractor receives an unexpected W-9, he or she should pause before filling it out and investigate whether the requester has a legitimate reason for requesting this form. When financial institutions need to report dividends or interest, they may use Form W-9 to request information from customers. Be cautious: the financial institution should have your tax ID number from when you opened the account. Another situation in which you should be cautious before completing Form W-9 is if the company requesting it is your employer and you are supposed to be classified as an employee rather than an independent contractor.
What is backup withholding?
If the IRS has informed a contractor that they are subject to "backup withholding," the businesses paying the contractor's invoices must withhold and remit income tax at a flat rate of 24% from the invoice. If a contractor is subject to backup withholding, they must specify it on their W-9.
What is the Most Secure Way to Submit Form W-9?
It's best if you can deliver the document in person. Otherwise, you can use a free online service to encrypt your completed Form W-9 and securely email it to the requester. You could also use a file-sharing service that is encrypted. Another option is to send it via FedEx, UPS, or the postal service, though there is no guarantee that it will not be lost, stolen, or tampered with in transit. There's also no guarantee that the recipient will store the form securely even if you send it securely, so inquire about their storage method before sending. When you choose us for cloud-based accounting services, you gain access to the latest bookkeeping and accounting technology in the market.
Can I Refuse to Fill Out Form W-9?
If you refuse to comply with a legitimate request, your client will withhold 24% of your pay. The IRS requires businesses to obtain a completed Form W-9 from anyone they pay $600 or more to during the year. Fines may be imposed for failure to comply. However, if you believe the person requesting the form has no right to request it, refusing it is probably a good idea. If you are concerned, seek advice from a tax professional.
W-9 forms are commonly used in a variety of situations, most notably for independent contractors or freelancers. It is critical that you fill out the form correctly because you may face penalties if you do not. All of the information, however, should be relatively easy to obtain. Take care to protect your sensitive information and accurate tax reporting status when distributing the form to the requesting party. You will receive accurate and trustworthy accounting services from our team of certified professionals, along with the top online bookkeeping services you've been looking for.